Accomack County, Virginia
| Accomack County, Virginia | ||
|
||
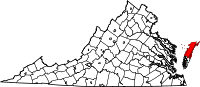 Location in the state of Virginia |
||
 Virginia's location in the U.S. |
||
| Founded | 1671 | |
|---|---|---|
| Seat | Accomac | |
| Area - Total - Land - Water |
1,310 sq mi (3,393 km²) 455 sq mi (1,178 km²) 855 sq mi (2,214 km²), 65.25% |
|
| Population - (2000) - Density |
38,305 83/sq mi (32/km²) |
|
| Website | www.co.accomack.va.us | |
Accomack County, formerly Accomac Shire, is a U.S. county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2000 census, the population was 38,305. Its county seat is Accomac[1].
Accomack and Northampton Counties comprise the Eastern Shore of Virginia, part of the Delmarva Peninsula.
Contents |
History
Accomac Shire was established in 1634 as one of the original eight shires of Virginia. The shire's name comes from the Native American word Accawmack, meaning "on the other side".[2] In 1642 the name was changed to Northampton by the British, to eliminate "heathen" names in the New World. Northampton was split into two counties in 1663. The northern section assumed the original Accomac name, the southern, Northampton. In 1940, the General Assembly officially added a "k" to the end of the county's name to arrive at its current spelling. The name of "Accomack County" first appeared in the Decisions of the United States Board on Geographical Names in 1943.[3]
The first Sheriff in the United States, William Stone, was appointed to serve Accomack County in 1634.
In 1670, the Virginia Colony's Royal Governor William Berkeley abolished Accomac County, but the Virginia General Assembly re-created it in 1671.[4]
Unlike most of Virginia, during the Civil War, the county was not under Confederate control, but held by the forces of the United States government.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,310 square miles (3,393 km²), of which 455 square miles (1,179 km²) is land and 855 square miles (2,214 km²) (65.25%) is water.
Transportation
- Accomack County Airport
Adjacent counties
- Somerset County, Maryland - northwest
- Worcester County, Maryland - northeast
- Northampton County, Virginia - south
- Middlesex County, Virginia - west (water boundary only, in Chesapeake Bay)
- Lancaster County, Virginia - west (water boundary only, in Chesapeake Bay)
- Northumberland County, Virginia - west (water boundary only, in Chesapeake Bay)
National protected areas
- Assateague Island National Seashore (part)
- Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Martin National Wildlife Refuge (part, Watts Island portion)
- Wallops Island National Wildlife Refuge
Demographics
As of the census[5] of 2000, there were 38,305 people, 15,299 households, and 10,388 families residing in the county. The population density was 84 people per square mile (32/km²). There were 19,550 housing units at an average density of 43 per square mile (17/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 63.38% White, 31.56% Black or African American, 0.33% Native American, 0.22% Asian, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 3.57% from other races, and 0.89% from two or more races. 5.38% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 15,299 households out of which 28.90% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.20% were married couples living together, 14.40% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.10% were non-families. 27.70% of all households were made up of individuals and 12.50% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 2.96.
In the county, the population was spread out with 24.30% under the age of 18, 8.20% from 18 to 24, 26.20% from 25 to 44, 24.70% from 45 to 64, and 16.70% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females there were 94.30 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.00 males.
Accomack and adjacent Northampton County are the two poorest counties in the Commonwealth of Virginia.[6]
Towns
|
|
Education
The county is served by Accomack County Public Schools[7].
The schools in this district are[8]:
Elementary Schools
- Accawmacke Elementary School
- Chincoteague Elementary School
- Kegotank Elementary School
- Metompkin Elementary School
- Pungoteague Elementary School
Middle Schools
High Schools
- Arcadia High School
- Chincoteague High School
- Nandua High School
- Tangier Combined School
- Badger Technical Center
Notable residents
- William Anderson, born in Accomack County, United States Congressman from Pennsylvania[9]
- Thomas Evans, (c.1755-1815), born in Accomack County, United States Congressman from Virginia[9]
- George T. Garrison, (1835-1889), born in Accomack County, member of Virginia state legislature and United States Congressman from Virginia[9]
- James Hamilton, (c.1710-1783), born in Accomack County, lawyer and mayor of Philadelphia[9]
- James Henry, (1731-1804), born in Accomack County, lawyer and delegate to the Continental Congress[9]
- Abel P. Upshur, (1790-1844), born in Accomack County, United States Secretary of the Navy and United States Secretary of State.
- Henry A. Wise, (1806 - 1876), born in Accomack County, United States Congressman, United States Ambassador to Brazil, Governor of Virginia, and Confederate General.
References
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Template.cfm?Section=Find_a_County&Template=/cffiles/counties/usamap.cfm. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. pp. 23. http://books.google.com/books/pdf/The_Origin_of_Certain_Place_Names_in_the.pdf?id=BqwPAAAAIAAJ&output=pdf&sig=3IVIg6u-evPGlrv4j1uDL7rQ09c.
- ↑ Topping, Mary, comp., Approved Place Names in Virginia: An Index to Virginia Names Approved by the United States Board on Geographic Names through 1969 (Charlottesville, VA: University Press of Virginia, 1971), 1.
- ↑ Accomack County, Virginia Genealogy, History and Records
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ Accomack and Northampton County EC on USDA Rural Development
- ↑ Education, Virginia Department of (2009). "Virginia Public School Division Staff". Virginia Department of Education. http://doe.virginiainteractive.org/vdoe_directories/StaffBySchoolDivisions.aspx?d=1&w=true. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- ↑ Accomack County Public Schools (2008). "Accomack County Public Schools - Eastern Shore of Virginia". Accomack County Public Schools. http://www.sbo.accomack.k12.va.us/public/school/. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Who Was Who in America, Historical Volume, 1607-1896. Chicago: Marquis Who's Who. 1963.
External links
 |
Somerset County, Maryland | Worcester County, Maryland |  |
|
| Chesapeake Bay | Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Northampton County |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
